Sodium Carboxymethyl-Cellulose – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/16/2017 / By Rita Winters

Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, commonly known as cellulose gum or CMC, is a type of stabilizer and thickener used in food like milk, ice cream, and some baked goods. Other uses include laundry detergents, chemicals, paper and ink making, dyeing, and oil drilling. As a cellulose, it is made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen molecules, which are all found in plant matter. Cellulose gum comes from wood pulp cell walls. It has two grades: food grade and industrial grade. There are different types of cellulose gum purity, but only purified (99.5 percent) cellulose gum is safe to eat.
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is basically a food additive used in cooking. It can serve as a bulking agent, an emulsifier, a firming agent, gelling agent, glazing agent, humectant, stabilizer, and thickener. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classified it as a Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) substance; however, we need to be wary of its various uses, and the purity of the cellulose gum used in our food. Food cooked or prepared with cellulose gum may have a decreased nutritional value, especially in large amounts. In some food labels, cellulose gum is classified as a fiber, even if it is not, and has no nutritional value at all. It should be noted that CMC is highly processed.

List of known side effects
Since cellulose gum is indigestible, your stomach and intestines will not be able to break it down and absorb it.
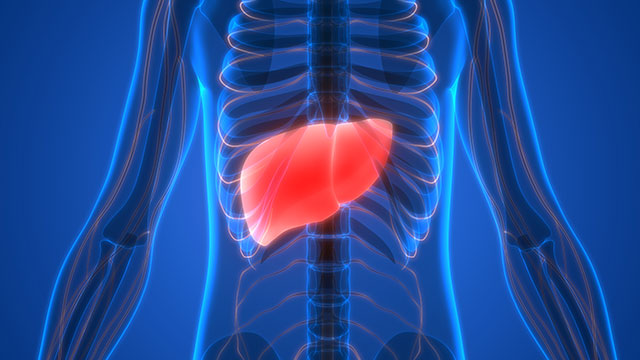
Body systems affected by sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
Laboratory organisms including rats, guinea pigs, mice, and rabbits showed a lot of side effects when exposed to sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. Some of the laboratory subjects developed reproductive disorders, tumor growth, and caused inflammation.
Furthermore, cellulose gum is an additive, and not a real food ingredient. While being accepted as a “safe” additive, there are possible risks that have not been discovered yet. Allergic reactions to cellulose gum are rare, but are happening in some areas around the world.
Large amounts may result in abdominal discomfort and bowel disorders (diarrhea, constipation).
Items that can contain sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
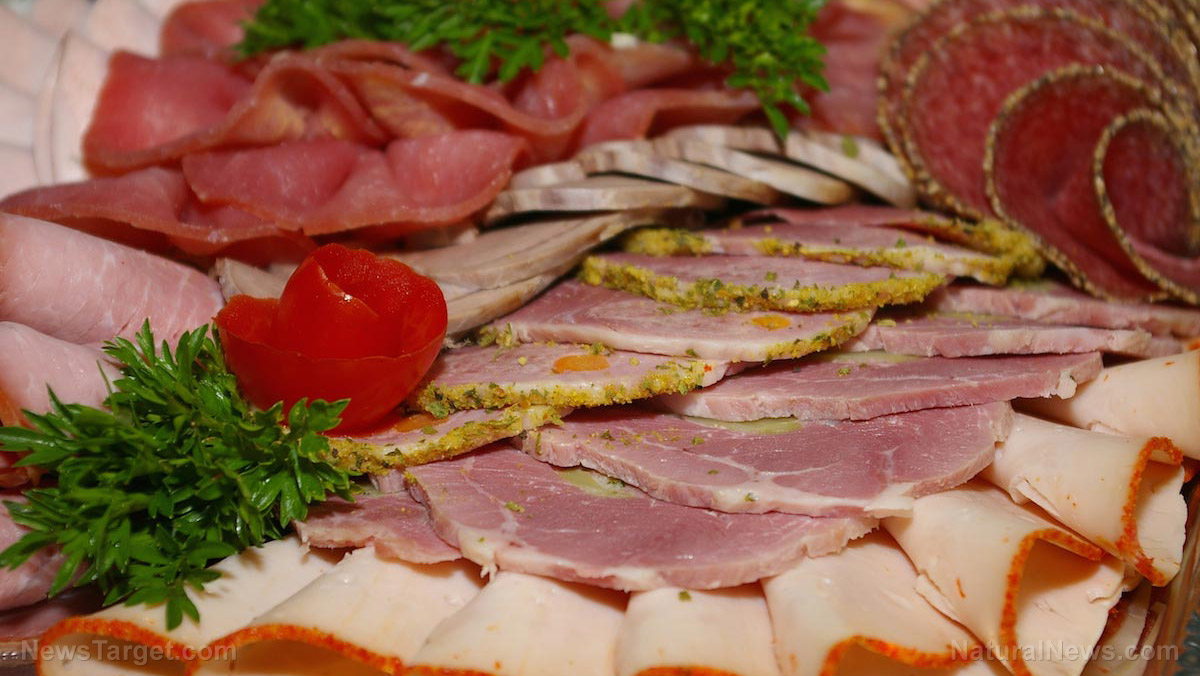
In food, CMC can be found in: ice cream, chocolate milk, cocoa, eggnog, condensed milk, powdered milk, cheeses, processed fruit, cereals, sausages, custards, etc.
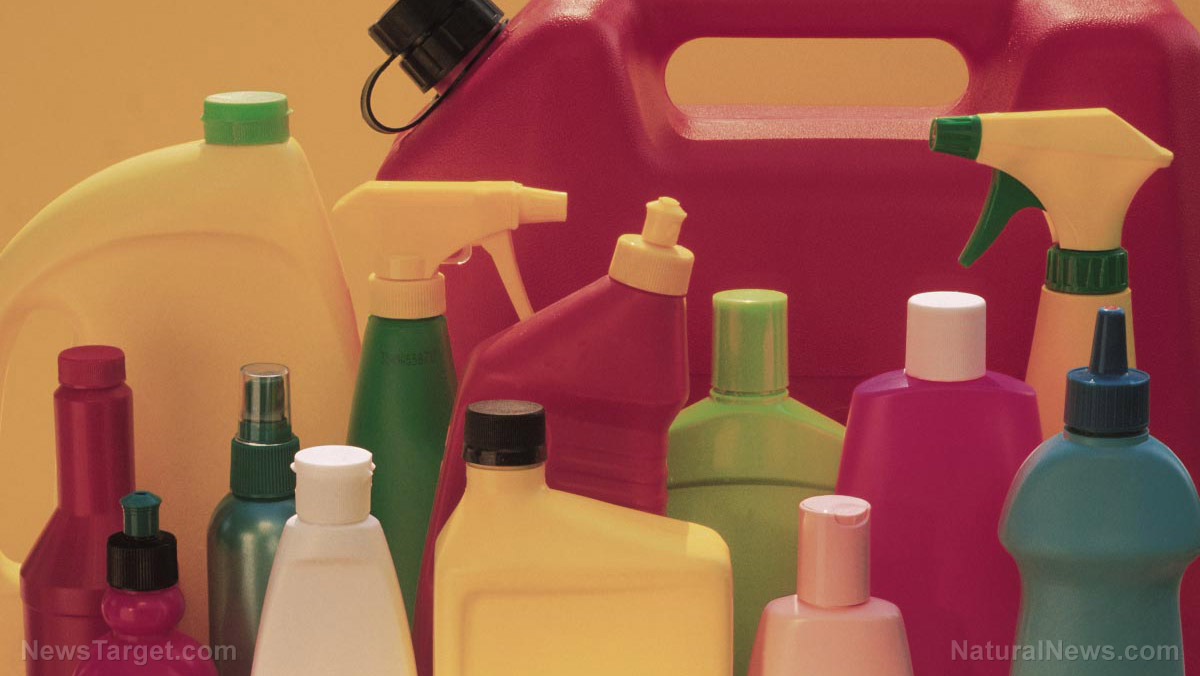
In everyday household items, it can be found in: lotions, shampoos, liquid soaps, creams, and other cosmetic products.
Other items that may include cellulose gum are: reusable ice packs, eye lubricants, gels, oil drills, and other viscous substances.
How to avoid sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
Avoid items as listed above, and watch out for labels that include microcrystalline cellulose (MCC), cellulose gel, cellulose gum, sodium salt, CMC, and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose.
Where to learn more
- Warning: Avoid Walmart’s Great Value Unmeltable Ice Cream Sandwich At All Cost
- There’s wood in my food? Wood-derived ingredients common in processed food
- Four solid reasons to avoid Starbucks
- Fiber helps control weight by releasing anti-appetite molecule acetate
- Shamrock Shakes! – Green No. 3 & More!
Summary
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, commonly known as cellulose gum, is a known food additive.
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose may be deemed safe, but large amounts may result in digestive system discomforts such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, and constipation.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: sodium carboxymethyl cellulose