Clothianidin – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/08/2017 / By Rita Winters

Clothianidin is a neonicotinoid pesticide similar to thiamethoxam and imidacloprid. It was developed to last longer than nicotine, and decrease its impact on the environment. However, it is highly toxic to honey bees, like most chemical pesticides. Clothianidin is an alternative to organophosphate, carbamate, and pyrethroid pesticides. It is developed by Takeda Chemical Industries and Bayer AG, and is registered in the following countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Canada, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, France, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Ireland, Japan, Korea, Lithuania, Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, Portugal, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, UK, and the United States.
Other names and synonyms of clothianidin include: 1-[(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)methyl]-2-methyl-3-nitroguanidine; CAS 210880-92-5; EC 433-460-1; EC 606-701-3; Guanidine, N-(2-chloro-5-thiazolyl)methyl-N’-methyl-N”-nitro-, (E)-; (E)-clothianidin; 1-(2-chlorothiazol-5-ylmethyl)-2-nitro-3-methyl-guanidine; and (E)-1-(2-Chloro-1,3-thiazole-5-ylmethyl)-3-methyl-2-nitroguanidine.

List of known side effects
Clothianidin is a chemical pesticide that can cause many negative effects on humans. Poisoning may occur through inhalation, dermal contact, and ingestion. Regulatory authorities describe the toxicity of clothianidin as extensive, and many studies have urged authorities to review the use of this chemical.
Laboratory tests reveal that clothianidin shows relatively low toxicity to many test species but is highly or extremely toxic to others (including honey bees). The toxicity of clothianidin varies, depending on the length of exposure.
From 2007 to 2011, there have been 12 cases of neonicotoid insecticide poisoning. According to the case reviews, the symptoms included: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, headache, and mild sedation. Mild poisoning can also cause dermal and eye irritation. Cases of severe poisoning included symptoms such as agitation, seizures, metabolic acidosis, coma, hypothermia, pneumonitis, respiratory failure, hypotension, ventricular dysrhythmia, and death.
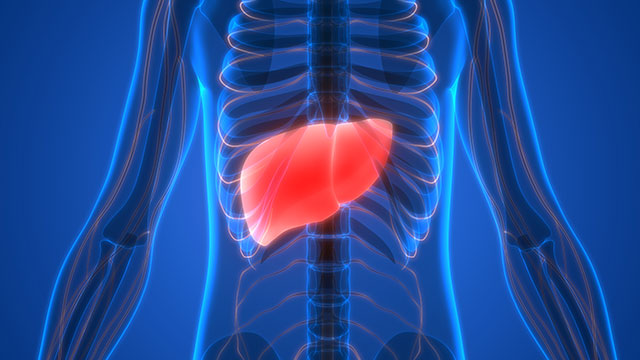
Body systems affected by clothianidin
Not likely to be carcinogenic to humans. According to lab tests, it may be genotoxic, teratogenic, and mutagenic, but further studies are needed.
Items that may contain clothianidin
Clothianidin is used in the following food crops: almonds, wine grapes, walnuts, broccoli, cauliflower, tomatoes, cabbage, lettuce, cantaloupe, spinach, bell peppers, potatoes, melons, pomegranates, sweet potatoes, watermelons, cucumbers, pecans, celery, kale, Brussels sprouts, collards, mustard, pears, artichokes, squash, and peaches. It may also be used to kill pests in ornamental plants.
This chemical is present in 33 registered chemicals in the U.S., some of which include Aloft gc g insecticide; Arena 0.25 g insecticide; Clothianidin technical insecticide; Poncho 600; Prosper t400 insecticide and fungicide seed treatment; and V-10170 0.25 g gl insecticide.
How to avoid clothianidin
Clothianidin is used in many commercial agricultural farms in many countries. Exposure to this chemical is likely in those areas. Fortunately, it is not registered for use in residential areas, therefore civilian risk is unlikely. Occupationally, clothianidin handling requires protective gear such as chemical gloves, boots, long-sleeved chemical suit, goggles, and a respiratory mask (full-face). Proper hygiene must always be practiced before and after handling toxic chemicals. Keep clothianidin in a locked storage, inaccessible to unauthorized and untrained personnel.
Where to learn more
- Germany Bans Eight Pesticides Linked to Honeybee Population Collapse; Clothianidin Chemical Found Contaminating Dead Bees
- For the first time, bee-killing neonicotinoid pesticides are now being found in drinking water
- Top German supermarket bans neonicotinoid pesticides linked to mass honeybee deaths
- Syngenta asks EPA to raise insecticide limits while scientists develop robots to replace bees decimated by chemicals
- EPA acknowledges deadly effects of pesticides on bees, but refuses to restrict their use
Summary
Clothianidin is a chemical pesticide known to cause a vast array of negative effects on humans.
Clothianidin is deadly if ingested.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: clothianidin