Calcium Propionate — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/07/2017 / By Jhoanna Robinson

Calcium propionate is a food additive that has uses as a preservative in bread and other baked goods. For optimal results, it can be combined with propionic acid and sodium propionate. The United States Food and Drug Administration classifies it under the category generally recognized as safe (GRAS).
This substance is very important in the food industry due to its fungistatic effect, meaning it can prevent the accumulation of mildew in foods such as bakery products. It hinders even naturally occurring bacteria from feeding since it blocks the enzymes that bacteria need for growth.

List of known side effects
Calcium propionate is associated with the inducement of migraine headaches. Fermented foods, which naturally make calcium propionate, have been known to cause headaches.
Body systems affected by calcium propionate
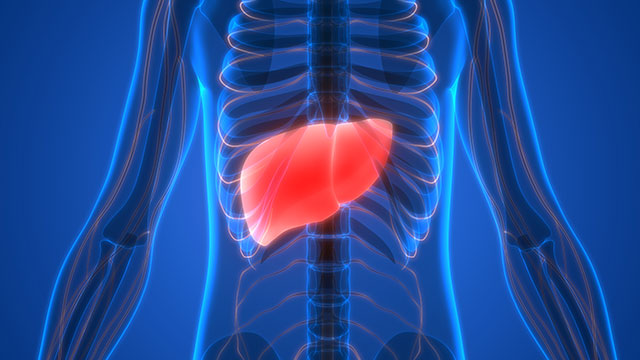
Calcium propionate is bad for the digestive system. While not directly causing the inflammation of the stomach lining, it has effects on your stomach’s ability to heal inflammation, thereby making the healing process a lit bit longer. It can cause permanent damage to your stomach lining by heightening the effects of gastritis and inducing several ulcers.
Items that can contain calcium propionate
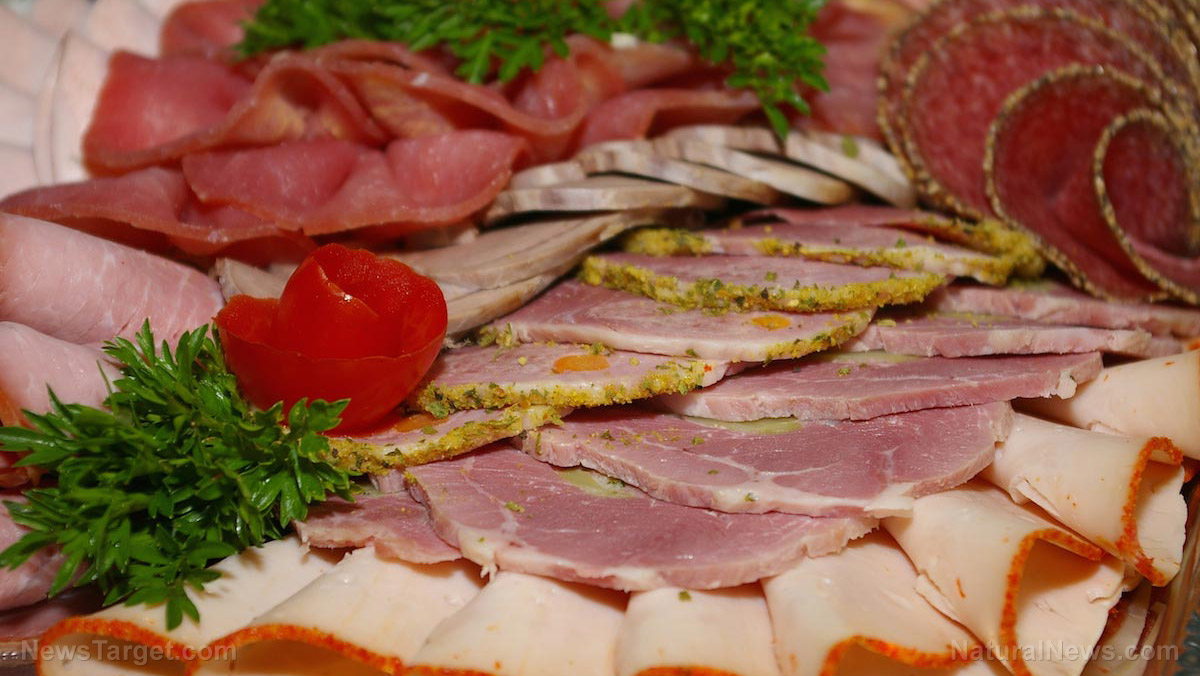
Foods that contain calcium propionate include baked goods, dairy, dairy products, egg, fat-based desserts, processed meat (including canned fish and shellfish), and vegetable products. Calcium propionate is also naturally contained in butter and some cheeses such as Swiss cheese or Emmentaler.
Calcium propionate is also used in beverages and sports drinks. Also, it can be found in malt beverages such as cider, distilled spirits with more than 15 percent alcohol, beer, and malt beverages. It also preserves the life span of feed grains.
As a quick aside, since calcium propionate doesn’t need to be extracted from an animal source, it is considered extremely vegan-friendly. However, it is not recommended for pregnant women and lactating mothers.
How to avoid calcium propionate
Always check the ingredients list of any product that has been deemed likely to include calcium propionate. Veer away from ingesting said products, or if that is not possible, eat very minimally of such. Opt for fresh bread, albeit it has a shorter life-span, than bread that is engineered to last for days.
Where to learn more
- Are You Being Poisoned On a Daily Basis?
- Why McDonald’s Happy Meal hamburgers won’t decompose – the real story behind the story
- Fast food meal remains unchanged after two years sitting on counter; bugs and fungi avoid toxic, junk food
- Edible film made from essential oils can protect foods better than plastic
- Pet Food Ingredients Revealed!
Summary
Calcium propionate is bad for the digestive system.
Foods that contain calcium propionate include baked goods, dairy, dairy products, egg, fat-based desserts, processed meat (including canned fish and shellfish), and vegetable products. Calcium propionate is also used in beverages and sports drinks.
It is not recommended for pregnant women and lactating mothers.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: calcium propionate