Acetone — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
12/07/2017 / By Earl Garcia

The Agency for Toxic Substances & Disease Registry (ATSDR) website classifies acetone as a manufactured chemical. According to the entry, the toxic substance can also be found in nature. The volatile organic compound comes in many other names including dimethyl formaldehyde and dimethyl ketone.

List of known side effects
Acetone poisoning can occur through various external causes such as inhalation, ingestion, and direct skin and eye contact. The harmful chemical is known to primarily target the central nervous system. According to a Med Line Plus entry, acetone exposure may result in drowsiness, confusion, reduced consciousness, and lack of coordination. Likewise, the hazardous substance may induce a feeling of drunkenness, lethargy and slurred speech, and even coma. A Pub Chem article stresses that acetone may cause severe eye irritation as well.
The chemical is also associated with an increased risk of hypotension or low blood pressure levels. In addition, acetone is found to trigger an onslaught of digestive system disorders. Exposure to the toxic substance may cause nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Victims who suffer from acetone poisoning are known to exude a fruity odor and carry a sweet taste in the mouth. Furthermore, acetone poisoning is shown to affect both the respiratory and urinary tracts. Inhaling the harmful chemical may result in shortness of breath and reduced breathing rate. The toxic substance is also associated with increased urination.
The chemical evaporates rapidly and is highly flammable. Thus, acetone is widely considered as a significant threat to environmental health.
Body systems affected by acetone
Acetone is particularly detrimental to the central nervous system’s overall health. Likewise, the hazardous chemical affects both cardiovascular and digestive health. The compound is also highly toxic to the respiratory tract and the urinary system.
Items that can contain acetone
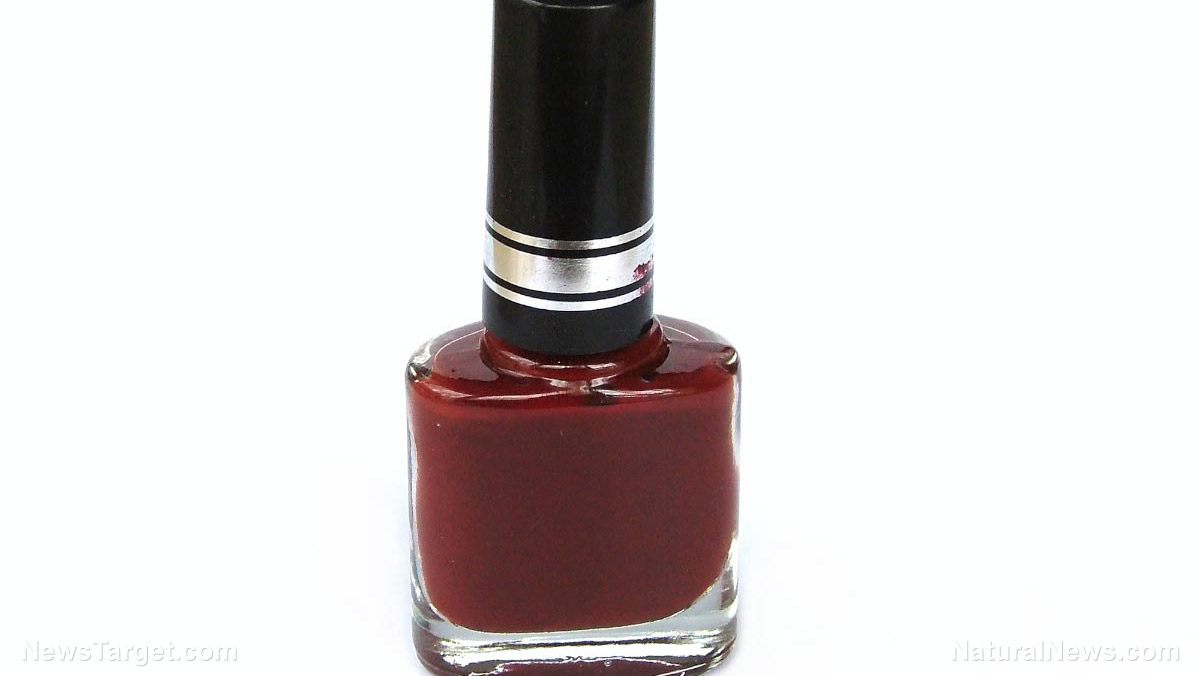
Acetone occurs naturally in plants, tree,s and volcanic gases as well as vehicle exhaust, tobacco smoke and landfill sites. Likewise, the chemical is commonly added to various cosmetic and industrial products including nail polish remover, cleaning solutions, and glues. The compound is also a primary chemical component of rubber cement and some lacquers.
How to avoid acetone
An article posted on the Health Line website recommends a few ways to prevent acetone exposure. These tips include:
- Keeping spaces well ventilated when using acetone-based or acetone-containing products
- Wearing a face mask when using acetone products in places with inadequate ventilation
- Wearing protective eye wear in order to prevent direct eye exposure
- Keeping acetone-containing products away from children’s reach
- Storing the highly flammable chemical away from flames or direct heat
People exposed to the toxic chemical are advised to call a poison control center and to seek immediate medical attention. Likewise, it is important to note the following factors at the event of an accidental ingestion:
- The victim’s age, weight and condition
- Product name and ingredients
- Time of chemical ingestion
- The amount that the victim ingested
Where to learn more
- BREAKING: CDC confirms Natural News 100% CORRECT on report of African Green Monkey kidney cells used in vaccines
- Skin care expert reveals the 20 most toxic chemical ingredients in beauty products… are you poisoning yourself?
- Study: Toxic chemicals in makeup, plastics and other everyday products are harming unborn babies, damaging the brain and reducing IQs
- Dove’s ‘natural’ beauty products contaminated with cancer causing chemicals, fake dyes and toxic fragrances
- Mothers suffering from toxic chemical exposure more likely to have autistic and ADHD children, research suggests
- Nail polish users exposed to chemical linked to paralysis, reproductive disorders, study finds
Summary
Acetone exposure causes drowsiness, confusion, reduced consciousness, and lack of coordination.
Acetone poisoning also results in feeling of drunkenness, lethargy and slurred speech, and even coma.
Acetone induces digestive conditions including nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Acetone raises the odds of reduced breathing rate, labored breathing, and increased urination.
Acetone is particularly detrimental to the central nervous system’s overall health.
Acetone negatively affects both cardiovascular system and digestive health.
Acetone is highly toxic to the respiratory tract and the urinary system.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Acetone