Metamitron — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/29/2017 / By Zoey Sky

Metamitron is a synthetic compound which belongs to the chemical group the Triazinones. Metamitron is an herbicide and it is selective and systemic when in action. Metamitron can be used on pre-emergence or post-emergence weeds. It appears as yellow crystals and is available in a variety of formulations such as wettable powders and water-dispersible granules.
Metamitron is applied as a foliar spray, and it is absorbed effectively via the leaf surface and the roots. Metamitron is often used on target plants like weeds of fodder beet, mangels, red beets, and sugar beets. These include grasses and broad-leaved weeds.
Metamitron can be used on its own, or in various combinations with other common sugar beet protection products, namely desmedipham, ethofumesate, and phenmedipham. It is also known as Goltix, 41394-05-2, Herbrak, Metamiton, Methiamitron, DRW 1139, Methiamitron [French], Methiamitron [Belgium], BAY-DRW 1139, Metamitrone [ISO-French], EINECS 255-349-3, BRN 0613129, and CHEBI:6791.

List of known side effects
Metamitron is harmful if swallowed, and it is very toxic to aquatic life. A known fire hazard, metamitron gives off irritating or toxic fumes (or gases) in a fire. As for its chemical dangers, metamitron decomposes on heating. This produces toxic fumes including nitrogen oxides.
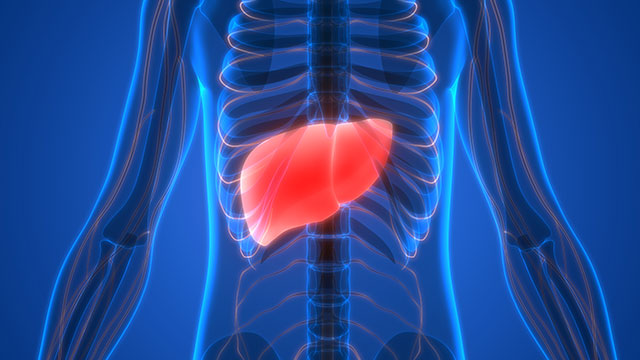
Body systems affected by metamitron
Metamitron was reviewed at a meeting of experts for mammalian toxicology (PRAPeR 54, round 11) in July 2008. Since there were no detailed impurity profiles of the batches used in the different tests available, no conclusion on the equivalence of the batches used in the toxicological tests with the technical specification of metamitron can be drawn. The experts determined that the purity of the batches used in the toxicological tests and that of the technical specification of metamitron is very high.
Metamitron is absorbed rapidly; peak plasma levels are already attained 20-40 minutes after application, and almost completely absorbed based on excretion in urine (34-56 percent) and bile (55-65 percent). It is rapidly and evenly distributed in the blood and various organs of the body.
While higher tissue residues were found in the liver and the kidneys, there is no evidence of a potential for accumulation. Excretion is rapid at more than 90 percent within 48 hours via urine and feces. Metamitron is rapidly and extensively metabolized since only less than 4.3 percent of metamitron have been recovered in excreta as such.
Metabolism involves an initial desamination step followed by hydroxylation, oxidation, and conjugation reactions. Major metamitron metabolites found in urine and feces of rats are metamitron-triazinium acetic acid, metamitron-4-hydroxy-desamino, metamitron-3-hydroxy-desamino, and desamino-metamitron.
Items that can contain metamitron
Metamitron is a herbicide that is effective against grass and broad-leaved weeds in beet crops. It is used to control pests such as grasses and broad-leaved weeds. Metamitron is usually applied on sugarbeets, fodder beets, mangel, and red beets. The herbicide was first reported in 1975.
How to avoid metamitron
When handling metamitron, remove and wash contaminated clothing and gloves, including the inside, before re-use. Wash hands before breaks and immediately after handling metamitron. When using, do not eat, drink, or smoke.
For respiratory protection, use a filter respirator or self-containing breathing apparatus. For eye protection, wear a face-shield. Provide an emergency eyewash fountain and quick drench shower in the immediate work area.
For hand protection, use PVC or other plastic material gloves when dealing with the concentrate or spray. To protect the skin, wear suitable (chemical resistant) overalls and closed footwear at all times.
Do not let metamitron enter the environment and sweep spilled substance into covered containers. If appropriate, moisten first to prevent dusting then carefully collect the remainder. Store and dispose of according to local regulations.
Where to learn more
Summary
Metamitron is a synthetic compound that belongs to the chemical group the triazinones.
Metamitron appears as yellow crystals and is available in a variety of formulations (e.g. wettable powders and water-dispersible granules).
Metamitron is harmful if swallowed, and is very toxic to aquatic life.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: metamitron