Fipronil — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/29/2017 / By Michelle Simmons
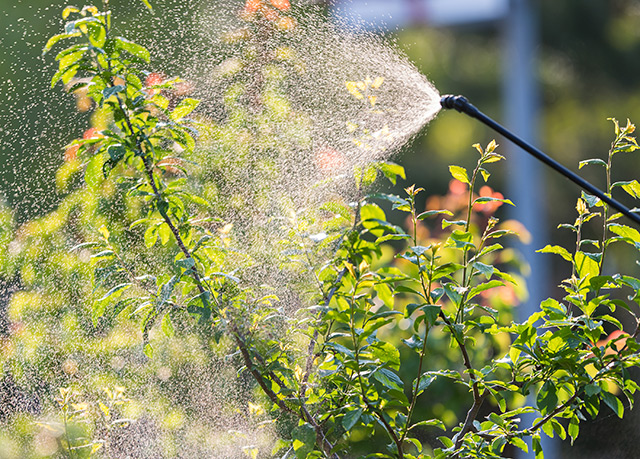

Fipronil is an insecticide that belongs to the group of phenylpryazole chemicals. It is used to eliminate ants, beetles, cockroaches, fleas, ticks, termites, mole crickets, thrips, rootworms, weevils, and other insects. This insecticide is most commonly used on rice crops and to treat rice seeds. Moreover, it is an ingredient in some tick and lice control medications for pets. Fipronil works by interrupting the normal functioning of the central nervous system in insects when they eat it or come in contact with it. Like other phenylpryazole chemicals, it inhibits GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) gated chloride channels in nerve cells. This stop the intake of chloride ions, which overstimulates nerve cells and cause paralysis and death. This insecticide was first registered for use in the United States in 1996. Fipronil can be described as a white powder with a moldy odor that has a low solubility in water and does not bind greatly with soil. Fipronil has the molecular formula of C12H4Cl2F6N4OS.
List of known side effects
Fipronil can cause many side effects in humans. A person can be poisoned by fipronil. Similar to other phenylpryazole chemicals, it mainly affects the central nervous system. The most common symptoms of fipronil poisioning include ataxia or uncoordinated movements, hyper-reactivity or exaggerated reaction to stimuli, tremor or uncontrolled trembling or shaking movements, cramps or sudden, involuntary contractions of muscles, convulsions, abnormal gait, and seizure. Other symptoms include twitching, nodding, aggression, sweating, nausea, lack of appetite, vomiting, headache, abdominal pain, dizziness, agitation, and weakness. Fipronil may also cause local dermatitis or skin irritation with pruritus or itching, and erythema or red skin. It may also cause irritation on the eyes. Prolonged or repeated exposure to the chemical may bring damage to the body organs exposed. The exposure routes of the insecticide are through contacting with the skin, contacting with the eyes, breathing the chemical in, or ingesting them. Fipronnil is also a possible cause of cancer in humans.
In a rat study on fipronil exposure, long-term exposure to fipronil caused an increase in seizures and death among the test animal. Moreover, it was found to reduce thyroid hormone levels among rats. In a different study, researchers discovered that long-term exposure to the insecticide can affect the reproductive system of the rats. Its effects included less mating, decreased fertility, smaller litter size, and higher loss of pregnancy. It also lowered the survival rate and slowed down the development among offspring.
For its environmental side effects, it has been found to be extremely toxic to fish, aquatic invertebrates like shrimp and water fleas, and to the aquatic environment. Fipronil was also found to be toxic to some birds, but not ducks, and to honey bees.
Body systems affected by fipronil
There are several body systems that the herbicide ethofumesate can adversely affect. These body systems include the nervous, muscular, ocular, integumentary, reproductive, respiratory, and digestive systems.
Items that can contain fipronil
Some of the products that can contain fipronil are pesticide products, such as granular products for grass, gel baits, spot-on pet care products, liquid termite control products, and products for agriculture. Some of the products that can contain ethofumesate can be identified under the trade names of Goliath Gel, Vi-Nil, Regent 500FS, Regency, and Sofion.
How to avoid fipronil
In order to avoid exposure to fipronil, it is important to always follow the label instructions of products containing the chemical. In addition, it is essential to use personal protective equipment when working with the insecticide. To avoid skin contact, it is important to wear full-length work clothes. Another way to avoid skin contact is to wear waterproof gloves. Eye protection is not normally required, but it is advised to refrain from touching the eyes while handling the product.
Where to learn more
- Pesticides continue to contaminate US streams, USGS report says
- Illegal application of pesticides in Indiana leads to widespread contamination of restaurants, nursing homes
- STUDY: Urban ‘dust’ laced with insecticides
- More proof: Pesticides are killing honeybees
- Top 10 Foods For Your Eyes
Summary
Fipronil is a phenylpryazole insecticide that is used to control insects, such as ants, beetles, cockroaches, fleas, ticks, termites, mole crickets, thrips, rootworms, and weevils.
Fipronil poisoning can cause ataxia, hyperreactivity, tremor, cramps, convulsions, abnormal gait, and seizure.
Fipronil poisoning may also cause twitching, nodding, aggression, sweating, nausea, lack of appetite, vomiting, headache, abdominal pain, dizziness, agitation, and weakness.
Fipronil may irritate the skin, eyes, gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory tract.
Fipronil is a possible human carcinogen.
Fipronil affects the nervous, muscular, ocular, integumentary, reproductive, respiratory, and digestive systems.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Fipronil