Zoxamide – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/23/2017 / By Rita Winters

Zoxamide is a man-made compound that controls blights like leaf blight, antracnose, downy mildew, and bunch rot dead arm. It is a fungicide that is used on potatoes, grapes, tomatoes, cucurbitacae species including gourd, melons and squash, onions and garlic. It has a rainfast preventive action, meaning it cannot be washed away by rain, and leaves residue. Zoxamide controls fungi by inhibiting nuclear division such as mitosis and cell division. It is a fine white powder that can be mixed with other compatible chemicals. Since it leaves residue. This chemical has low toxicity in humans, however, is highly toxic to aquatic life forms.
Other names for zoxamide are 3,5-Dichloro-N-(1-chloro-3-methyl-2-oxo-3-pentanyl)-4-methylbenzamide; (RS)-3,5-dichloro-N-(3-chloro-1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-oxopropyl)-p-toluamide; and 3,5-dichloro-N-(3-chloro-1-ethyl-1-methyl-2-oxopropyl)-4-methylbenzamide. It’s CAS registry number is 156052-68-5. Zoxamide belongs to a class of chemicals known as dicholorbenzenes. It is a compound containing benzene with two chlorine atoms attached to it.
This fungicide is harmful if absorbed through the skin, eye, and through ingestion. Prolonged or frequent exposure may result in histopathological changes in internal organs, and acute dermal problems such as dermatitis, sensitization and allergic reactions. Occupational exposure may result in inhalation of the powder chemical. However, zoxamide rapidly metabolizes and can be eliminated by the bile and excreted with feces.

List of known side effects
Zoxamide is a fine, white powder that may be inhaled, absorbed through the skin and eyes, and may be ingested. It can cause dermal allergies, sensitization, and rashes. Severe eye irritation may occur when exposed to large amounts of the powder.
Body systems affected by zoxamide
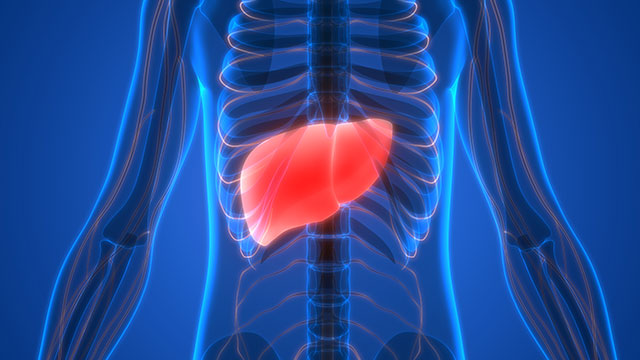
This chemical substance may cause an increase in the weight of the liver and thyroid. Zoxamide may also cause histophatological changes to the liver, and increase the human body’s alkaline phosphatase. It is highly toxic to aquatic life, and has long-lasting effects in water bodies, especially in still waters.
Items that can contain zoxamide
Food items that may contain zoxamide are potatoes, grapes, tomatoes, cucurbits including gourds, melons, and squash, as well as onions and garlic.
Other items that may contain zoxamide are farming equipment and protective clothing when administering the fungicide.
How to avoid zoxamide
To avoid exposure to zoxamide, precaution must always be exercised. When using zoxamide to treat blights, protective gear must always be worn. These include chemical-resistant gloves, boots, coveralls, and full-face gas masks. Protective gear must always kept within a storage facility in the workplace. Since zoxamide is highly toxic to water life, it must not be released into the environment and spills must be collected.
When exposed to zoxamide through inhalation, move to fresh air. On skin and eye contact, wash thoroughly and extensively with water. Upon ingestion, the mouth must be rinsed. If symptoms of toxicity or other side effects occur, immediately seek medical attention.
Where to learn more
- Be cautious with these fruits and vegetables; they’re known to contain the most pesticides
- Poison.news
- Chemicals.news
- Toxins.news
- Pesticides.news
Summary
Zoxamide has low toxicity but may affect the liver and and thyroid after prolonged exposure. It is a dermal sensitizer, which may cause allergic dermal reactions, dermatitis, and rashes.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: zoxamide