Sodium lauryl sulfate — toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/14/2017 / By Frances Bloomfield

Sodium lauryl sulfate, more commonly known as SLS, is a synthetic, organic compound present in a great variety of industrial and personal care products. Creating sodium lauryl sulfate involves extracting lauryl alcohol from either coconut oil or petroleum. Once extracted, the lauryl alcohol is then combined with sulfuric acid or sulfur trioxide gas to produce sodium lauryl sulfate.
This chemical can serve as an emulsifier, foaming agent, detergent, and surfactant, or substance that reduces surface tension and allows better interaction between liquids and solids. These qualities, combined with the fact that sodium lauryl sulfate is inexpensive to make, has made it a popular ingredient in everything from shampoos to engine degreasers to laundry soaps.

List of known side effects
Though often derived from coconuts, there are numerous health concerns over the inclusion of sodium lauryl sulfate. One such concern is that sodium lauryl sulfate can irritate the skin and eyes. Undiluted, this compound is an irritant, and even concentrations of just two percent can aggravate the eyes and skin. Rashes, dandruff, psoriasis, canker sores, cataracts, and dermatitis have all been linked to excess sodium lauryl sulfate exposure. This is why the International Journal of Toxicology has recommended sodium lauryl sulfate concentrations of no more than one percent.
While a certain percentage of sodium lauryl sulfate is generally considered safe, the body is unable to break down this compound, and can instead absorb it. This means that sodium lauryl sulfate can accumulate within the body over a certain period of time, and that these residual levels can eventually become much higher. More than just causing skin inflammation, these trace amounts of sodium lauryl sulfate can disrupt the natural balance of hormones by mimicking of hormones like oestrogen, a type of estrogen.
Whether in its pure form or as part of a product, sodium lauryl sulfate is combustible and can emit irritating or toxic fumes when heated. These fumes can contain sulfur oxides, which are sharp-smelling gases that can bring about coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Respiratory irritation may occur as well.
Sodium lauryl sulfate should never be consumed. Ingesting this compound can result in an individual experiencing nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Additionally, sodium lauryl sulfate is not known to bioaccumulate in the environment. It’s considered to be highly toxic to aquatic organisms, however, and may leave behind long-lasting effects.
Body systems affected by sodium lauryl sulfate
Even at modest amounts, sodium lauryl sulfate can harm the skin and eyes. Prolonged and frequent exposure can cause more damage to these organs, with cataracts and dermatitis being just some of the possible side effects.
Ingesting and inhaling sodium lauryl sulfate can be dangerous for the digestive and respiratory systems, respectively.
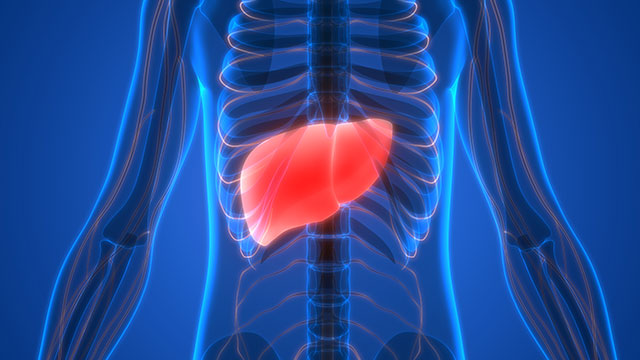
Traces of sodium lauryl sulfate have been found in the heart, lungs, brain, and liver, so it’s possible that sodium lauryl sulfate can harm these as well over a certain period of time.
Items that can contain sodium lauryl sulfate
Sodium lauryl sulfate, which is commonly found in personal care and beauty products, can be found in the following items:
- Body Washes
- Liquid Hand Soaps
- Mascara
- Moisturizers
- Mouthwashes
- Shampoos
- Skin cleansers
- Soaps
- Sunscreen And Sunblock Lotions
- Toothpastes
Sodium lauryl sulfate can also be found in:
- Carpet Cleaners
- Industrial-strength Detergents
- Laundry Detergents
- Stain Removers
How to avoid sodium lauryl sulfate
Due to how common sodium lauryl sulfate is, avoiding it can be somewhat difficult. Thankfully, numerous green or natural alternatives to sodium lauryl sulfate-containing products have cropped up over the years. These types of goods will usually have a label declaring them to be “SLS free”.
In addition to its widespread usage, sodium lauryl sulfate can go by a wide variety of other names. Be sure to look for any of these names on the ingredients list:
- Dodecyl Alcohol, Hydrogen Sulfate, Sodium Salt
- Dodecyl Sodium Sulfate
- Lauryl Sodium Sulfate
- Lauryl Sulfate Sodium Salt
- Sodium N-dodecylsulfate
- Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate
- Sodium Dodecylsulfate
- Sodium Lauryl Sulfate Ether
- Solsol Needles
- Sulfuric Acid, Monododecylester, Sodium Salt
Where to learn more
- Discover these seven remarkable foods that naturally enhance the health of your hair
- Hazardous chemicals found in your personal care products
- How Your Daily Makeup Routine Ages Your Skin and Poisons Your Body
- Is your shampoo harming your health?
- Natural Tips for Fresher Breath
Summary
Though most products with sodium lauryl sulfate contain a negligible amount of this chemical, it’s known to accumulate in the body and cause health problems in due time.
Sodium lauryl sulfate has the potential to irritate the skin, eyes, respiratory, and digestive systems, depending on the method of exposure and entryways.
Burning sodium lauryl sulfate or products with this chemical can release fumes that contain noxious sodium oxides.
Sodium lauryl sulfate is highly dangerous to aquatic plant and animal life.
Sources include:
TheNaturalPenguin.com
SLSFree.net
LiveStrong.com
CDC.gov
TheSpruce.com
PubChem.NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov
Tagged Under: Sodium Lauryl Sulfate