Petroleum oil – toxicity, side effects, diseases and environmental impacts
11/21/2017 / By Janine Acero

Petroleum oil is a flammable liquid consisting mainly of hydrocarbons, more often called crude oil, appearing as clear to very dark brown and black. It occurs naturally in deposits from under the earth’s surface that formed from plants and animals millions of years ago. Gasoline is a derivative of petroleum used as fuel.

List of known side effects
Accidental inhalation or ingestion of crude oil and its petroleum-based products can cause a number of adverse side effects, such as:
- Abdominal pain
- Blood in the stools
- Body weakness
- Burning in the nose, eyes, ears, lips, or tongue
- Burning of the esophagus
- Collapse
- Convulsions
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Extreme fatigue
- Labored breathing
- Lightheadedness
- Loss of consciousness
- Low blood pressure
- Severe headaches
- Skin blisters
- Staggering
- Throat burning and swelling
- Vision loss
- Vomiting (with or without blood)
- Weakness
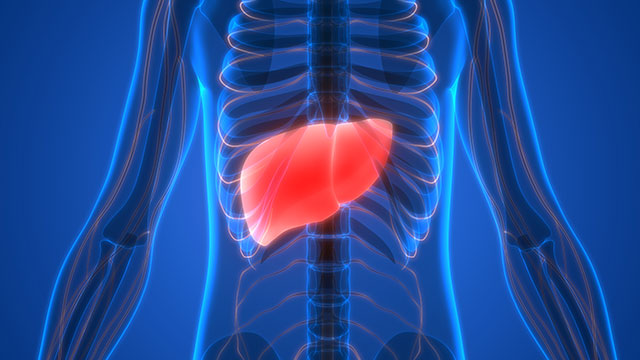
Body systems affected by petroleum oil
Swallowing crude oil or its derivatives or inhaling its fumes (mostly in occupational settings) may severely affect the liver, spleen and kidneys, as well as the respiratory, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, reproductive, and central nervous systems.
Items that can contain petroleum oil
Crude oil can be refined into many different petroleum-based products. Some of these are gasoline, distillates such as diesel fuel and heating oil, jet fuel, kerosene, petrochemical feedstocks, waxes, lubricating oils, and asphalt.
Some common household products also contain hydrocarbons. These are baby oils and suntan oils, and mineral oil based cosmetics like bath oils, creams, lotions, and makeup removers.
How to avoid petroleum oil
Since some common household products contain hydrocarbons, which are the main components of crude oil and its derivatives, it’s highly possible for children to make contact and be exposed to unsafe levels of these substances. According to Parents.com, it’s important to have basic poison prevention steps to protect your children. These are:
- Keep all chemicals and other substances out of reach of children, locked up and out of sight.
- Keep the items in their original containers.
- Close all containers securely after use to keep them child-resistant.
- Keep the original labels on the products and make sure to read the instructions for use beforehand.
- When using these products, keep young children within your line of sight, to make sure they don’t go near the substances.
- Decorative lamps and candles containing lamp oil should be kept out of reach of children.
- Don’t take medicine in front of children to make sure they don’t just take any substance on their own. Refer to medicine as “medicine”, not “candy”.
- Clean out the medicine cabinet periodically and safely dispose of unneeded and outdated medicines.
- Call your local poison center immediately in case of suspected or actual ingestion of chemicals.
Where to learn more
- Affordable Biofuel: An Evironmentally Friendly Alternative
- Electric cars just as dirty as petroleum-powered vehicles? New study sheds light on ‘zero emissions’ fraud
- The great algae conspiracy: Are oceans being destroyed to replace oil with algae?
- Oil giant BP agrees to pay largest criminal penalty in U.S. history for disastrous 2010 spill
- Are oil and water shortages manufactured in order to control the economy and human populations? A closer look at abiotic petroleum and primary water
Summary
Petroleum oil (crude oil) is a flammable liquid made up of hydrocarbons, which are substances that occur naturally from under the earth’s surface.
Gasoline is a derivative of petroleum oil used as fuel.
Crude oil can be refined into many petroleum-based products, including diesel fuel and heating oil, jet fuel, kerosene, lubricating oils, baby oils and suntan oils, bath oils, creams and lotions, to name a few.
Follow some basic poison prevention tips to protect your children from accidental exposure to these substances.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: crude oil, Petroleum oil